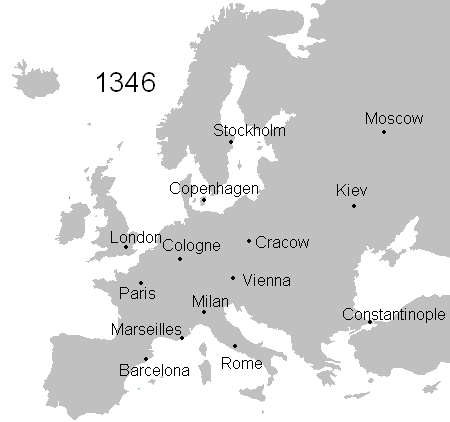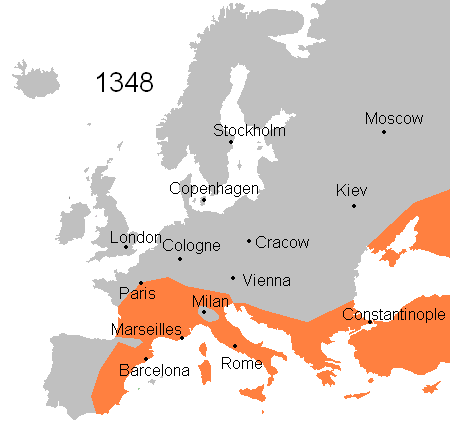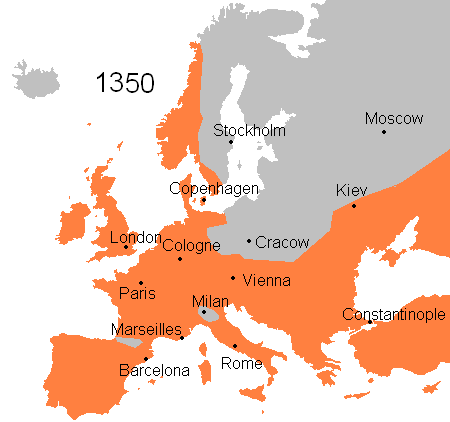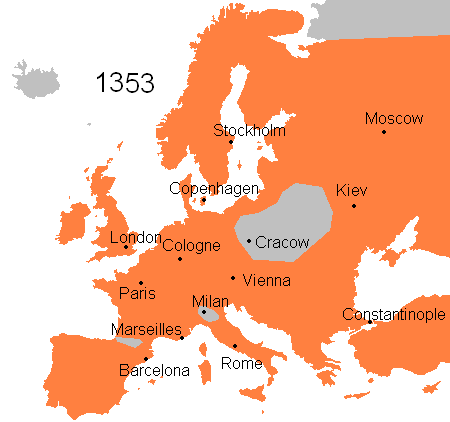
The Black Death was the second pandemic of bubonic plague and the most devastating pandemic in world history. It was a descendant of the ancient plague that had afflicted Rome, from 541 to 549 CE, during the time of emperor Justinian. The bubonic plague, caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, persisted for centuries in wild rodent colonies in Central Asia and, somewhere in the early 1300s, mutated into a form much more virulent to humans.
At about the same time, it began to spread globally. It moved from Central Asia to China in the early 1200s and reached the Black Sea in the late 1340s. Hitting the Middle East and Europe between 1347 and 1351, the Black Death had aftershocks still felt into the early 1700s. When it was over, the European population was cut by a third to a half, and China and India suffered death on a similar scale.
Traditionally, historians have argued that the transmission of the plague involved movement of plague-infected fleas from wild rodents to the household black rat. However, evidence now suggests that it must have been transmitted first by direct human contact with rodents and then via human fleas and head lice. This new explanation better explains the bacteria’s very rapid movement along trade routes throughout Eurasia and into sub-Saharan Africa.
At the time, people thought that the plague came into Mediterranean ports by ship. But, it is also becoming clear that small pools of plague had been established in Europe for centuries, apparently in wild rodent communities in the high passes of the Alps.
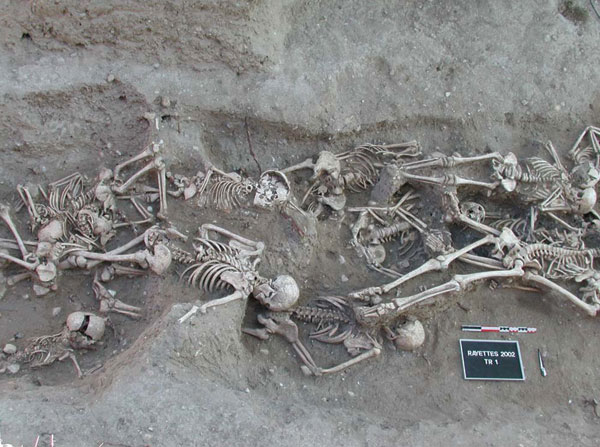

The remains of Bubonic plague victims in Martigues, France.
We know a lot about the impact of the Black Death from both the documentary record and from archaeological excavations. Within the last few decades, the genetic signature of the plague has been positively identified in burials across Europe.
The bacillus was deadly and took both rich and poor, rural and urban: the daughter of King Edward III of England died of the plague in the summer of 1348. But quickly—at least in Europe—the rich learned to barricade their households against its reach, and the poor suffered disproportionately.
Strikingly, if a mother survived the plague, her children tended to survive; if she died, they died with her. In the late 1340s, news of the plague spread and people knew it was coming: plague pits recently discovered in London were dug before the arrival of the epidemic.
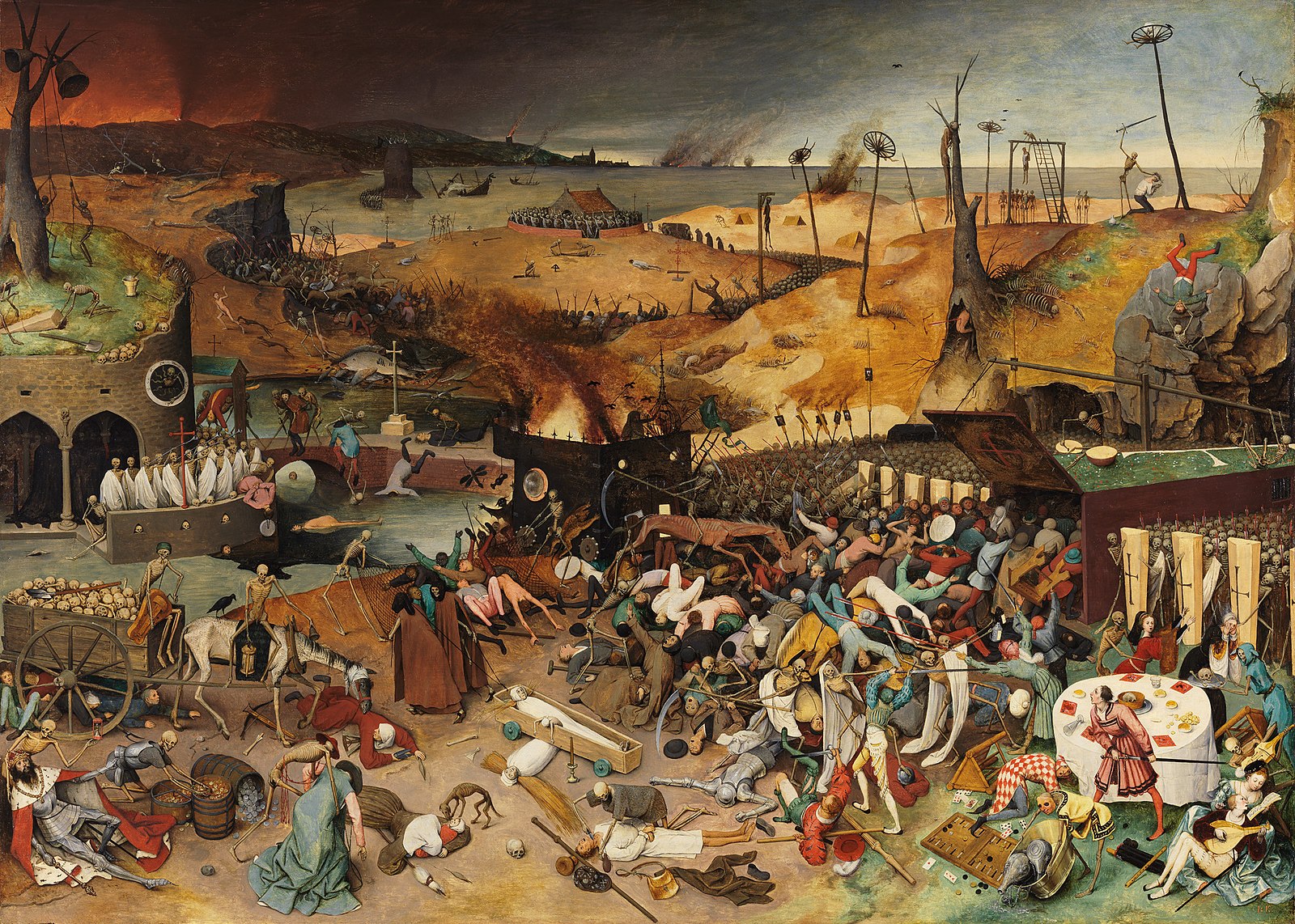

The Black Death pandemic was a profound rupture that reshaped the economy, society and culture in Europe. Most immediately, the Black Death drove an intensification of Christian religious belief and practice, manifested in portents of the apocalypse, in extremist cults that challenged the authority of the clergy, and in Christian pogroms against Europe’s Jews.
This intensified religiosity had long-range institutional impacts. Combined with the death of many clergy, fears of sending students on long, dangerous journeys, and the fortuitous appearance of rich bequests, the heightened religiosity inspired the founding of new universities and new colleges at older ones.
The proliferation of new centers of learning and debate subtly undermined the unity of Medieval Christianity. It also set the stage for the rise of stronger national identities and ultimately for the Reformation that split Christianity in the 16th century.

Depiction of the Great Plague of London in 1665 (left). A copper engraving of a seventeenth-century plague doctor (right).
The disruption caused by the plague also shaped new directions in medical knowledge. Doctors tending the sick during the plague learned from their direct experience and began to rebel against ancient medical doctrine. The Black Death made clear that disease was not caused by an alignment of the stars but from a contagion. Doctors became committed to a new empirical approach to medicine and the treatment of disease. Here, then, lie the distant roots of the Scientific Revolution.
Quarantines were directly connected to this new empiricism, and the almost instinctive social distancing of Europe’s middling and elite households. The first quarantine was established in 1377 at the Adriatic port of Ragussa. By the 1460s quarantines were routine in the European Mediterranean.
Major outbreaks of plague in 1665 and 1721 in London and Marseille were the result of breakdowns in this quarantine barrier. From the late 17th century to 1871 the Habsburg Empire maintained an armed “cordon sanitaire” against plague eruptions from the Ottoman Empire.
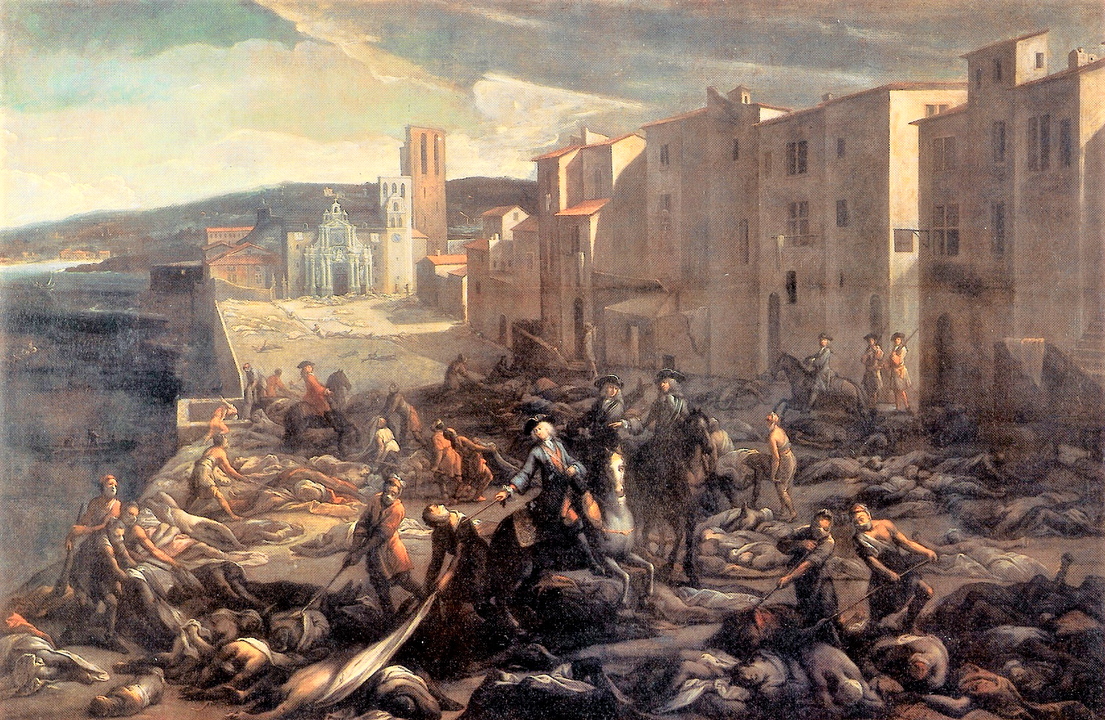

Michel Serre's painting depicting the 1721 plague outbreak in Marseille.
As with the rise of national universities, the building of quarantine structures against the plague was a dimension in the emergence of state power in Europe.
Through all of this turmoil and trauma, the common people who survived the Black Death emerged to new opportunities in emptied lands. We have reasonably good wage data for England, and wage rates rose dramatically and rapidly, as masters and landlords were willing to pay more for increasingly scarce labor.
The famous French historian Marc Bloch argued that medieval society began to break down at this time because the guaranteed flow of income from the labor of the poor into noble households ended with the depopulation of the plague. The rising autonomy of the poor contributed both to peasant uprisings and to late medieval Europe’s thinly disguised resource wars, as nobles and their men at arms attempted to replace rent with plunder.
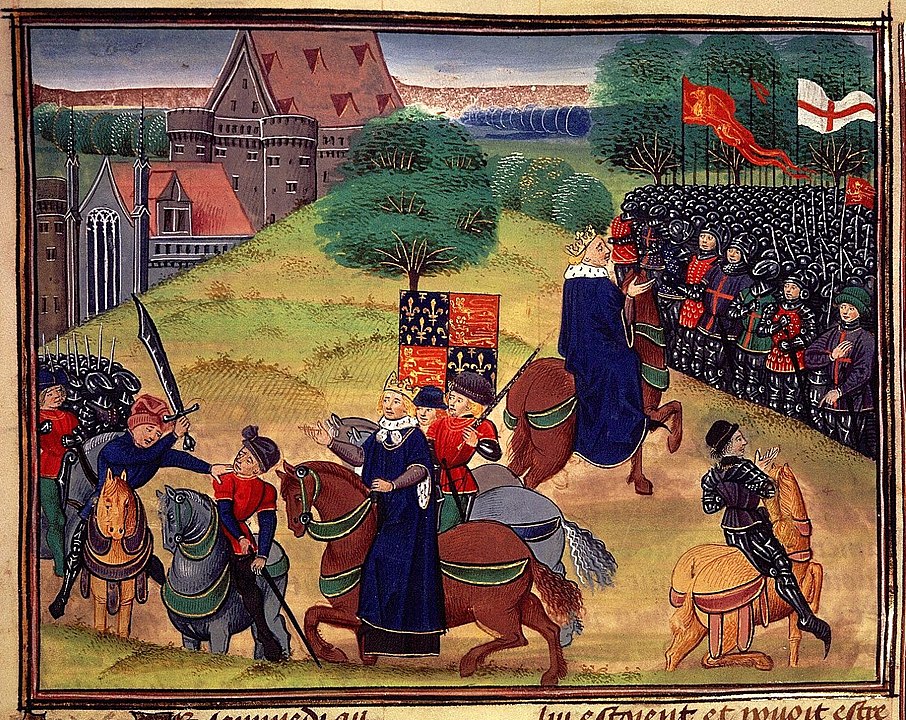

A depiction of the 1381 Peasant's Revolt in England.
At the same time, the ravages of the Black Death decimated the ancient trade routes bringing spices and fine textiles from the East, ending what is known as the Medieval World System, running between China, India, and the Mediterranean.
By the 1460s, the Portuguese—elbowed out of the European resource wars—began a search for new ways to the East, making their way south along the African coast, launching an economic globalization that after 1492 included the Americas.
And we should remember that this first globalization would lead directly to another great series of pandemics, not the plague but chickenpox, measles, and smallpox, which in the centuries following Columbus’s landing would kill the great majority of the native peoples of the Americas.
In these ways we still live in a world shaped by the Black Death.